When I first learned about FDM 3D printing, apart from searching the principles of 3D printer, the next thing I did was to explore the 3D printing material — filament.
Many questions flooded my mind, such as “What type of filament should be chosen for my first 3d print? Which filament is best for the next level when the printing skills have advanced…”
If you are also seeking the answers, let’s dive into the most common and popular types of 3d printing filament here together and impress your friends and family by getting perfect prints every time!
PLA Filament
With PLA, you can expect to see many different colors, as the filament is easy to customize. Moreover, PLA variants have emerged to meet growing aesthetic demands. You can even find filament that looks like wood grain, marble stone or comes with a glossy silky finish.
Click here to explore the magic of silk PLA.
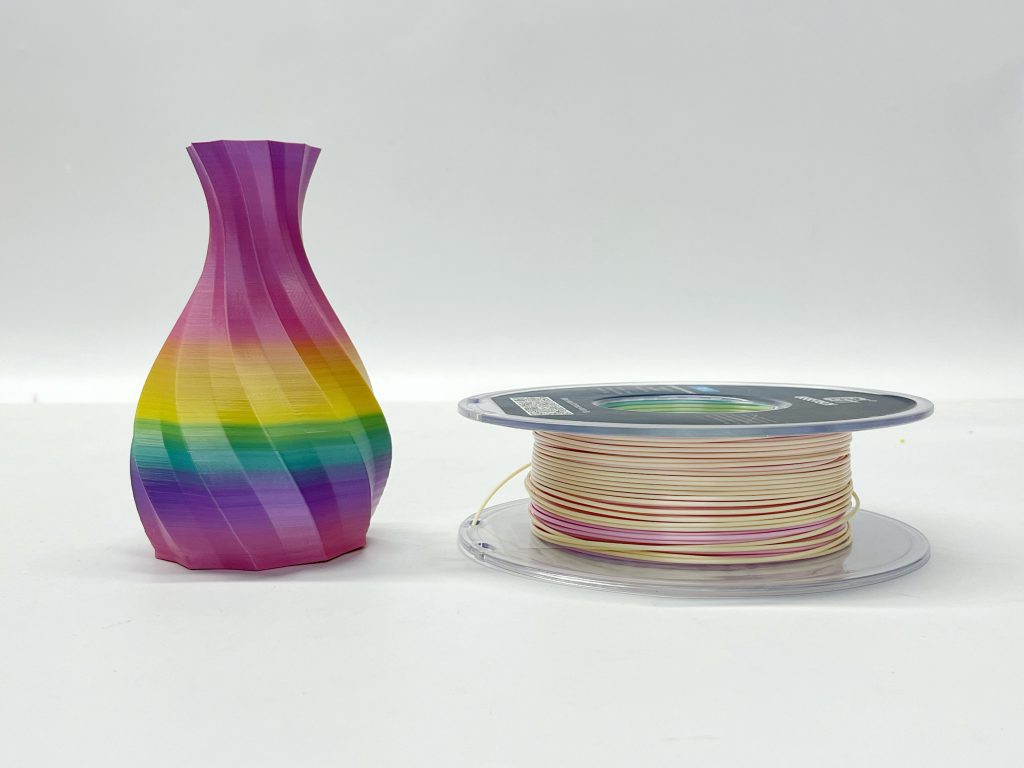

What Is PLA?
We recommend this type of 3D printer filament if you are looking for the best overall material or for your first print. If you are a beginner, PLA filament is a great choice; it requires no special printer settings and can be used for most types of prints that you find on common 3D model websites, and it is even widely recommended as “the easiest 3D printing material to print”.
The Properties of PLA Filament
You can also decide whether PLA suits your needs by assessing the required performance properties of the object that you want to print.
| Strength | Strong 3D printer filament |
| Temperature | Melts at ~185-215°C |
| Ease of Use | Beginner-friendly |
| Appearance | Smooth and shiny |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable 3D printing filament |
| Weaknesses | Not heat or water resistant |
| Safety | No fumes |
PETG Filament
Next on the list is PETG filament, which is easier to print than ABS and more durable than PLA.
If your printing skills have advanced from the new level, I will recommend PETG to you. You can find transparent filaments or glossy filaments with color, depending on what you prefer. An advantage here is that it can be in contact with food.
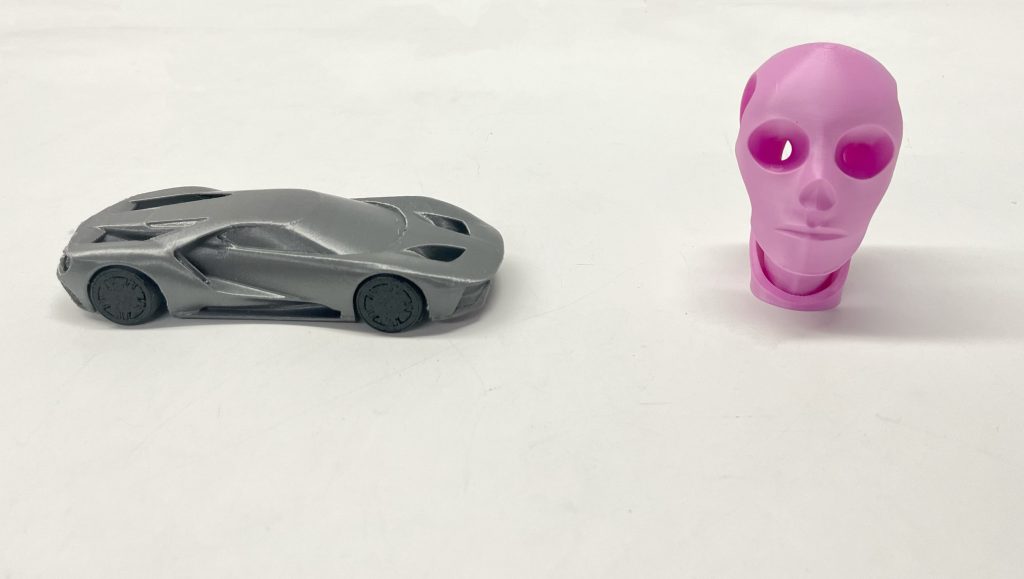

What Is PETG?
PETG(Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified) is often used in 3D prints designed to be placed outdoors. This is because the impact of the sun or temperature changes does not affect PETG as much as other types of filament. And more, PETG combines the key advantages of PLA’s printability and ABS’s durability.
The Properties of PETG Filament
PETG’s properties strike a balance between PLA and ABS.
| Strength | Strong and flexible |
| Temperature | Melts at ~220-240°C |
| Ease of Use | Moderate difficulty |
| Appearance | Glossy and clear options |
| Eco-Friendliness | Not biodegradable |
| Strengths | Durable and waterproof |
| Weaknesses | Prone to stringing |
| Safety | No fumes |
ABS Filament
ABS filament is often overlooked by people due to the pungent smell and high temperature requirements during the printing process.
But for special types of prints, such as high-heat-resistant automotive parts, Impact-resistant Lego pieces and so on, ABS is the best choice. Once you try it, you will be impressed by its remarkable heat resistance, impact toughness, mechanical strength and chemical stability. Read more below about its properties and uses.
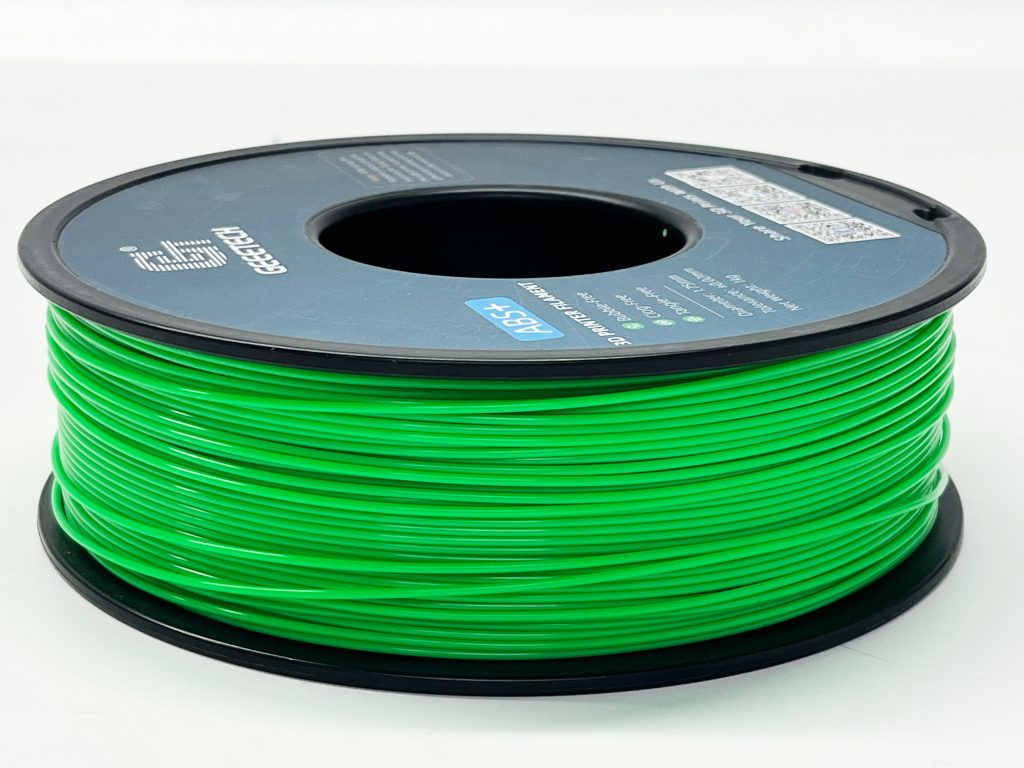

What Is ABS?
ABS filament is made from Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. When using ABS filament, you will get results that are able to stretch during printing, making it optimal for vase mode and other similar settings on your 3D printer. It gives you long-lasting prints that are durable.
The Properties of ABS Filament
Here are core properties of ABS.
| Strength | Strong and impact-resistant |
| Temperature | Melts at ~230-240°C |
| Ease of Use | Can be challenging to print with |
| Appearance | Matte finish |
| Eco-Friendliness | Not biodegradable |
| Strengths | Durable and heat-resistant |
| Weaknesses | Warps easily |
| Safety | Strong fumes |
TPU Filament
TPU filament is not used as frequently as some of the other filaments on our list, because of compatibility constraints, compared to the more commonly used Bowden Extruder on the market, TPU requires the Direct Drive Extruder for printing as it can more precisely control the retraction.
For applications where you need it to be soft or bendable, TPU can be an amazing option.

What Is TPU?
TPU can be used to make flexible and pliable parts such as connectors, belts, springs, phone covers, etc. The highly flexible material makes it possible to make prints with soft rubber properties, resulting in a flexible and elastic print.
The Properties of TPU Filament
People are often attracted by the softness of TPU.
| Strength | Flexible and tough like rubber |
| Temperature | Melts at ~200-230°C |
| Ease of Use | Challenging to Print |
| Appearance | Soft and matte finish |
| Eco-Friendliness | Not biodegradable |
| Strengths | Flexible and durable |
| Weaknesses | Requires precision |
| Safety | No fumes |
Which 3D Printer Material Is Right for You?
We made a comprehensive comparison as below:
| Material | When to Use It | Common Applications |
| PLA | For beginners or simple projects and when you need easy printing and smooth looks. | Toys, decorative items, models, prototypes. |
| PETG | For durable, water-resistant parts and when you need strength and some flexibility | Food containers, outdoor parts, mechanical components. |
| ABS | For toughness, heat-resistant parts and when durability and impact resistance matter. | Tool handles, automotive parts, enclosures, and functional items. |
| TPU | For flexible and stretchy objects and when elasticity and toughness are required. | Phone cases, gaskets, belts, toys, wearable items. |
Please keep in mind, that you are free to experiment and try out new combinations. This is just a guideline.
Which Material Is the Most Eco Friendly?
| PLA | 10/10 |
| PETG | 7/10 |
| TPU | 5/10 |
| ABS | 3/10 |
PLA is the clear winner here. It also uses less heat and therefore wattage for printing.
What Size 3D Print Filament Is Most Commonly Bought?
Typically, older 3D printers use a thicker filament, but newer technology has become more precise over the years, so 1.75 is now the standard.
| Filament Size | Properties | When to Use It |
| 1.75 filament | Most common, flexible, easy to use | Best for most 3D printers. |
| 2.85 filament (3 mm) | Thicker, stiffer, less flexible but strong | Used in older or specialized printers. |
Conclusion
The tables above mainly used reference products from Geeetech filament types, so different manufacturers might vary slightly in their values. All in all, the options above are considered among the most used for 3D printing filament types around the world and offer great value for money and print quality. Hope you have found your right 3d printing filaments after reading the article.