3D Bioprinting for Medical and Enhancement purpose
Let’s today discuss 3D Bioprinting. The most evolving subject of the 3D printing application. Hence, going forward we will discuss in-depth about 3D Bioprinting.
History of 3D Bioprinting
Why 3D Bioprinting?. In contrast, to the invention of SLA (stereolithography) in the year 1984 by ” Chunk Charles Hull“, and due to the lack of organ donors. 3D bioprinting came into the picture, 1988 when Doctor Robert J. Klebe presented his work Cytoscribing. Hence, a technique of micro-positioning the cells to create tissues in 2 or 3 dimensions using Inkjet printer.
As a result, a researcher from the University of Wake Forest Professor Anthony Atala followed the footsteps of Dr. Robert forged first bio-printed organ, that’s kidney in 2002.
In 2003, the first-ever 3d printing organs introduced. Due to the efforts done by Thomas Boland of Clemson University. As a result, he got patents for using Inkjet printing for cells.
The initial findings of him, cellular structures using 3D printing known-as Bioprinting. Therefore, led to the development in the production of tissues and organ structures. So, this led to more aggressive research in the field of organ transplants.
3D Printing Bio-Inks
The on-going development in the field of 3D printing is bioprinting which is one of the main sections of the additive manufacturing world. These bio-inks are helpful for patients who require transplants. Therefore, due to the lack of donors with an increasing number of patients need a transplant. To reduce these people started a journey towards bioprinting.
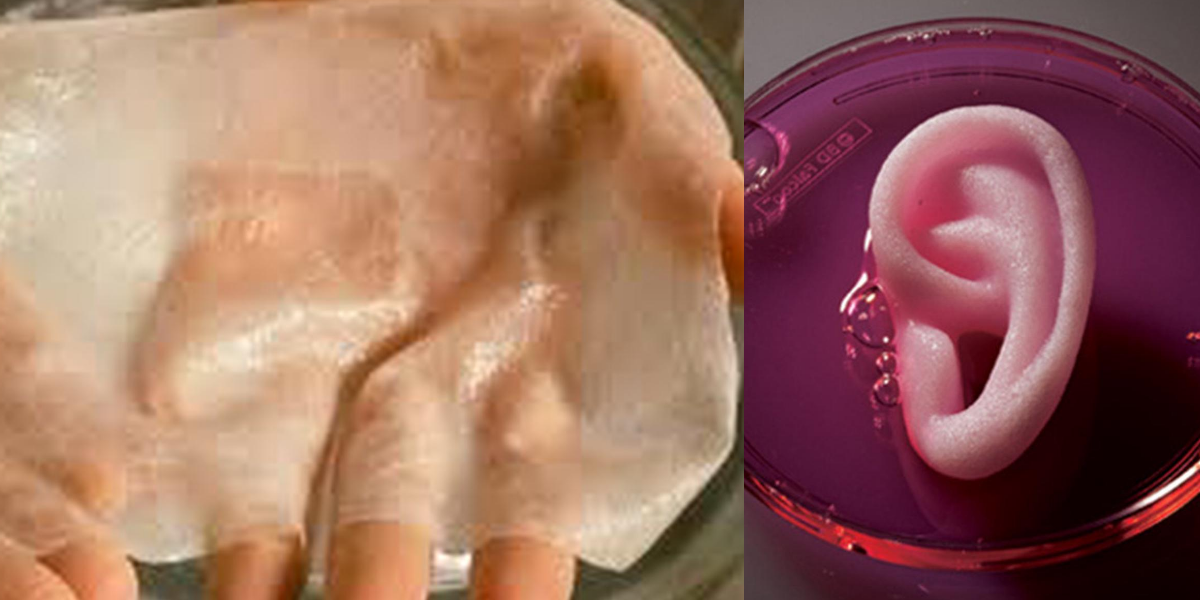
As a result, every year many people wait for a perfect matched transplant of the organ. That may take too long, even some of them die waiting for the transplant. So, there is a huge demand for the organs but, chances of getting them are lower than you even imagine. That’s how the story of patients require an organ transplant. As per the information provided by the World Health Organization in 2008. The data analyzed for 104 countries, that spoke for 90% of the population worldwide. Therefore, around 100,800 people needed solid organ transplants.
In 2018, one of the Biomedicine agency of France performed analysis. That data looks like 5,781 transplants performed while 22,000 patients are still waiting.
In The Making Of 3D Bio-Inks
Hence, you might be thinking what are these 3D bio-inks? In creating these bioprinting 3D printing plays an important role. Cells and biomaterials are paired together with layer-by-layer deposition to form cellular structures that certainly should have similar properties of the human tissues. Undergoing this process may require N-number of bio-inks to conceive the original tissue structure.
Furthermore, advancement is required in this field to successfully establish a human organ. If this is succeeded then it seems like the future of the medicine is going to rock the lives of the patients. So, for this many companies, universities, laboratories, and industries have already participated in this ongoing race.

Methods Of 3D Bio-printing
Above all, there are lots of challenges that one should face while printing the organs. The biggest challenge among them is high cost and people don’t have any idea or complete knowledge of it. There are several techniques to bioprinting those people came across let’s discuss them. Due to these new emerging methods may lead us to success.
Inkjet Bio-printer
The bioprinting technology is mostly based on classic inkjet prints. Therefore, even slight alteration made to FDM 3D printers. To obtain similar prints as that of inkjet printers. In this method, the bio-ink materials are deposited layer-by-layer and there are called biotins. On a hydrogel support or a culture plate, these biotins are placed.
The technology is even classified into thermal and piezoelectric method. Both methods are based on biotins. In thermal technology, heat helps to make air bubbles. When busted that provides pressure to vomit ink drops. Likewise, piezoelectric use electric charges that rack up in solid materials. In this method, piezoelectric polycrystalline ceramic present in each nozzle, if used too many damages cell membranes. Scientists successfully progressed in printing molecules, cells & membranes using this process, even stepped in the study of cancer & its treatment.
In 2010, the company named Organovo built the first laboratory of 3D printing. Organovo collaborate & started working with Invetech developers to create the first bioprint. Organovo being the leader linger bone tissue & liver tissue printing. The company uses inkjet prints and currently working on reproducing human tissue for the liver. That will repair the damaged parts of the liver, this will extend the life of the organ till the patients get a transplant.
SLA( Stereolithography)
The process has the highest precision in manufacturing. The technology uses ultraviolet light to stiffen the photopolymers. To control the light intensity the process uses digital micromirror arrays. Moreover, the process suitable for the production of layer-by-layer hydrogels that are sensitive to light. The printing time depends on the thickness of the print.
The disadvantages of using this method are more compared to others. The technique needs development due to a lack of biocompatibility & biodegradability of polymers. The harmful effects of toxic reagents, UV rays that may cause skin cancer, and unable to remove print medium structure.
Bioprinting By Extrusion
In this process, the biomaterial is extruded by coordinating the movement of a pressure piston or a micro-needle above a fixed support. The biomaterials used are generally solutions. We need to assemble the 3D model to complete it after the layer-by-layer extrusion. One of the advantages is that it provides room temperature treatment. The most popular bioprinters use this technique. It is the evolution of inkjet bioprinting like the EnvisionTec Bioplotter.
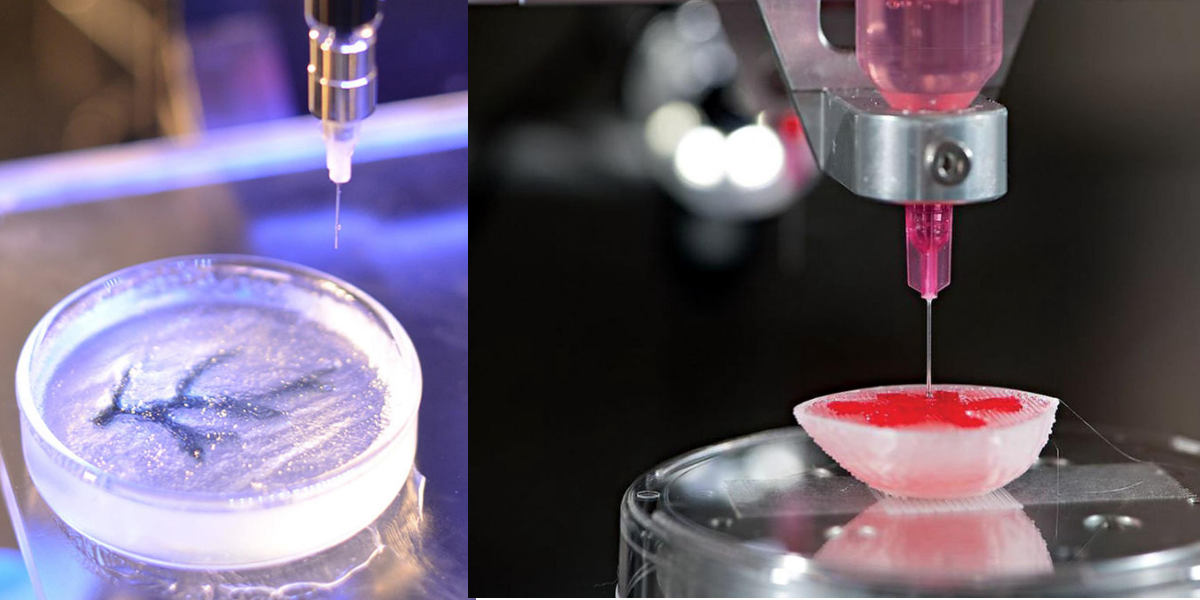

Laser Assistant Bioprinting
The process is distributed in 3 parts: a laser source, a plastic film of biological material and a receiver. The process uses a laser as the main source of energy to deposit biomaterial in a receptor. The illumination of film thus causes evaporation. The liquid biomaterial in the form of drops go-to receiver. The substrate contains a bio-polymer or cell culture to overcome cell adhesion. As a result, helps to develop them.
The unique advantage of laser bioprinting is the nozzle-free & contactless process. It also enables high-resolution cell printing & droplet control of biotin.
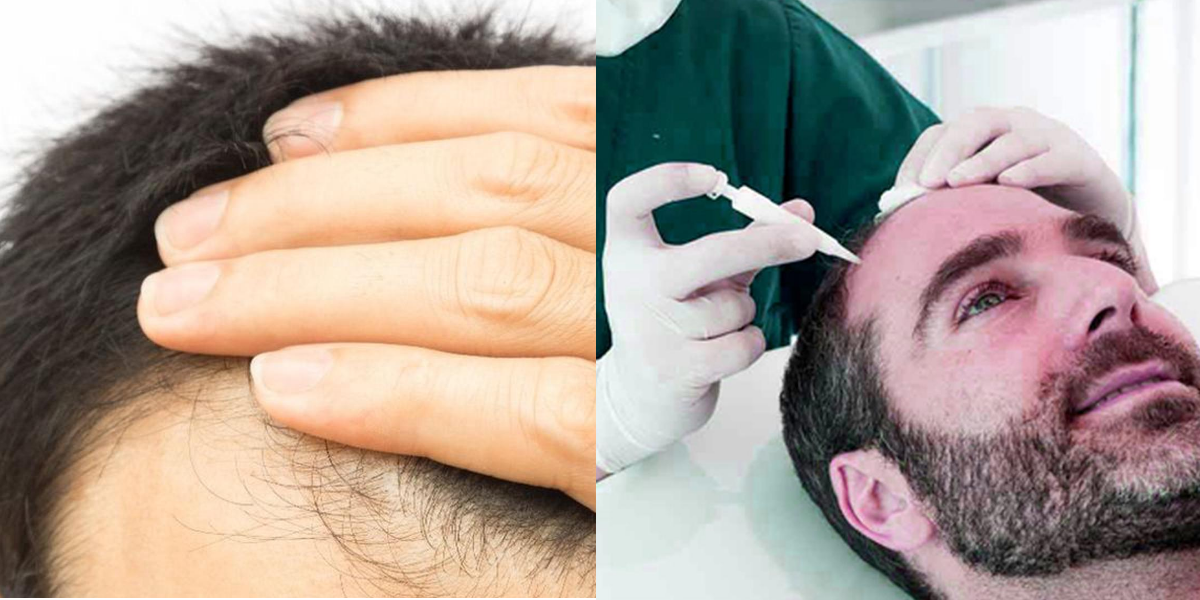
The French leader Poietis has successfully recreated hair in partnership with L’oreal. It allows precisely deposited cells in a particular geometry. Therefore French are even trying to recreate hair follicles. The solution for growing hair and alopecia problems.
Acoustic Wave Bio-printing
Uses kind of acoustic tweezers, a microfluidic system in which each cell is manipulated, and superficial acoustic waves. This process helped researchers to identify where the waves would meet. At the meeting point, waves form the knot which helps to capture individual cells. Then collected to form 2D and 3D models. The process provides high performance in terms of movement precision. The method was developed by Carnegie Mellon University, Pennsylvania State University, and MIT.
The technique needs development, a few months ago new application that is a functional ovary by the University of Northwest, in Illinois. Spanish researchers developed human skin. Hence, there are many more.
SWIFT Process
The abbreviation of SWIFT is Sacrificial Writing Into Functional Tissue. Process researched by Harvard Wyss Institute a new bio-printing technique. The method in which bio-impression of blood vessels on living tissue. It prints vascular channels in the living matrices composed of building blocks of organs taken from the stem cells. SWIFT is an easy process, which only focuses on printing the vessels. Those are build living tissue rather than creating an entire organ. The prints are made from the patient’s own cells. Used for therapeutic medicine to repair and replace human organs.
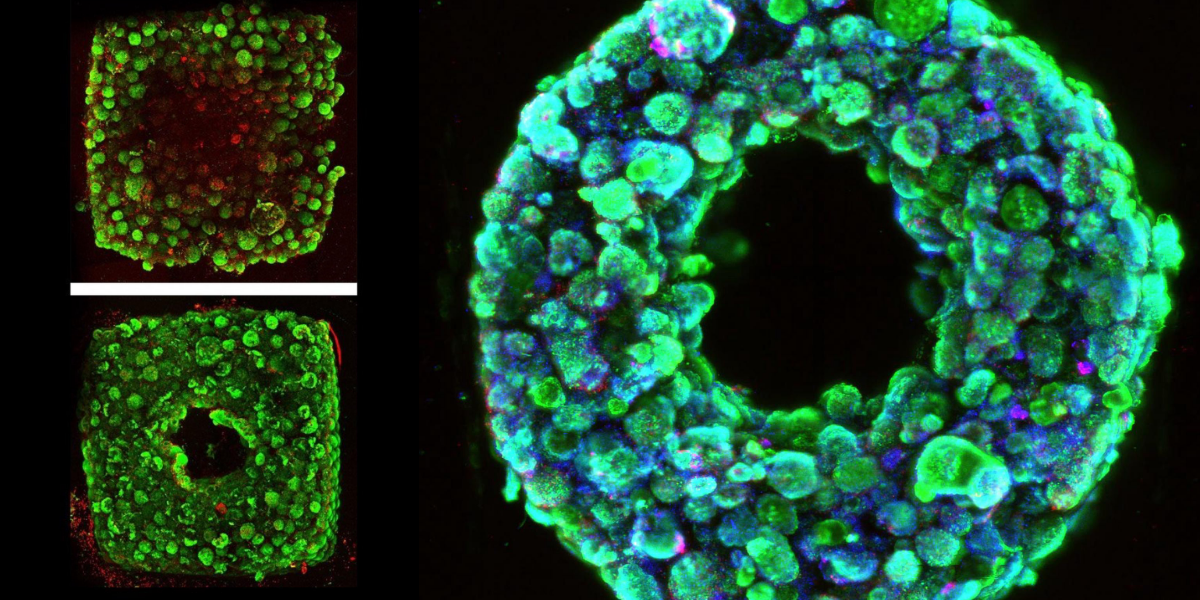
Problems Of 3D Bioprinting
The 3D bioprinting may cure the patients by all means, but only when there is a compatible match of the organ that needs to be transplanted. Even after, prefect compatibility if the body doesn’t support the artificial organ than what?. Still lot of research should be made on these aspects 3D bioprinting.
Another problem is speed and increase in the resolution. Higher resolution provides better interaction, compatibility, and control of 3D microenvironment. Speeding up may provide commercially available to all the needy.
The choice of the cell source is very important for bioprinting of the organs. If the choice of cell source is wrong then the entire process is in danger. So, the process needs more focus on all these aspects.
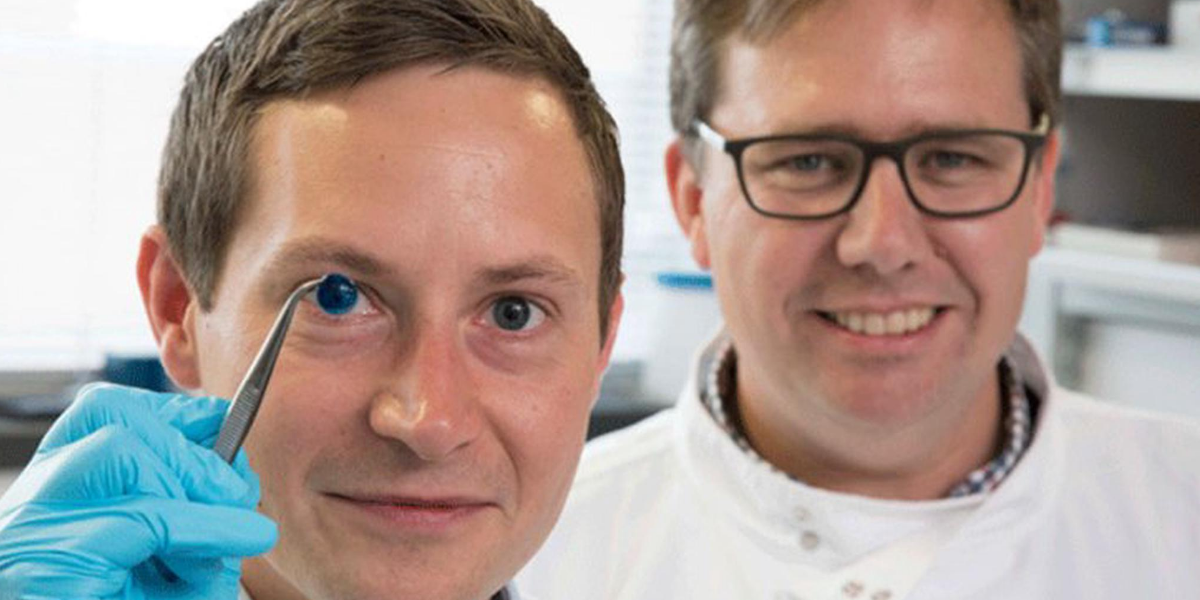

Future Of 3D Bioprinting
Bioprinting has a brighter future than any other technology. Due to its widespread applications in almost all the sectors. Now, even it is uplifting itself in the field of bioprinting. After successfully printing the heart, cornea, cartilage, bones, tissues, liver and skin. Still, it has a long way to go. With the help of other powerful technology AI, the researches and scientists can easily identify perfect cell sources, combinations of biomaterials.
In the upcoming decade, we might see the success of the 3D bioprinting. That will be considered as the greatest advancement in the medical field with more 3D prints, and organ transplants. In turn, going to help needy patients. There is still a lot to discover by the researchers and scientists. But, this dream will be true as soon as possible.
To know more about the latest innovations in 3D printing CLICK HERE.
Upcoming conference of 3D bioprinting. LEARN MORE
Make the best of Geeetech 3D printer only @ Geeetech official site
Video credit: TED-ED